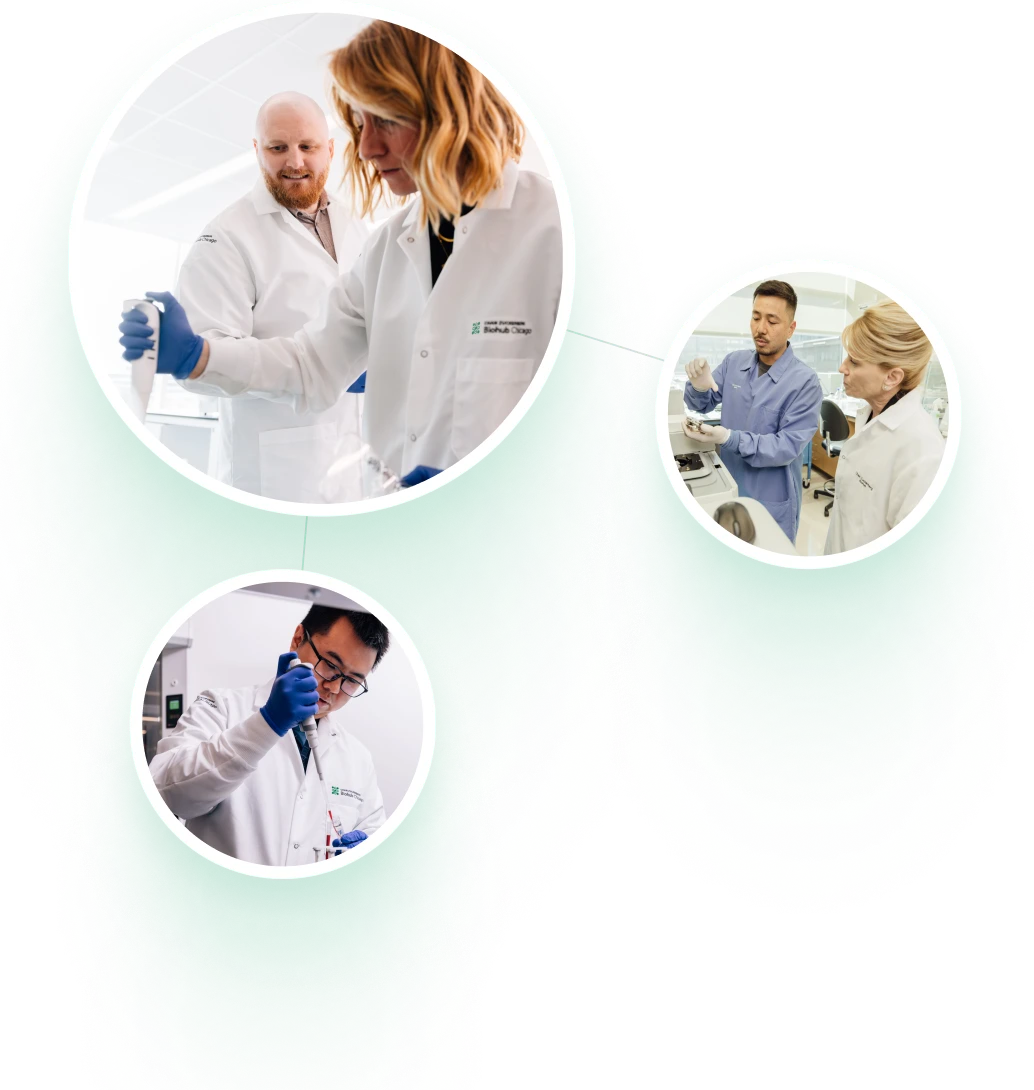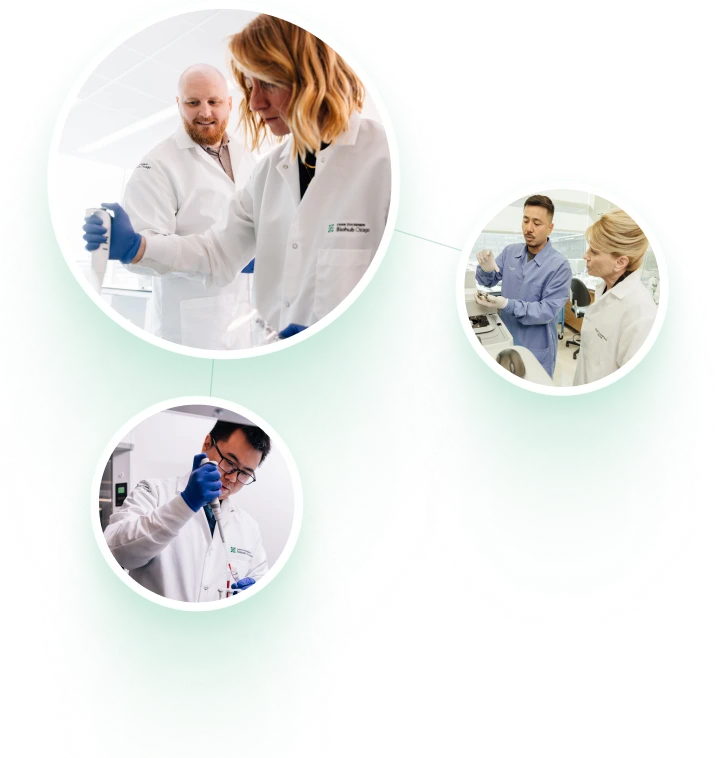
Creating New Technologies to Understand Inflammation and the Immune System
CZ Biohub Chicago is using a unique, engineering-driven approach to study human biology. By embedding thousands of sensors and sampling probes in tissues, scientists will be able to monitor molecular and cellular signals with unprecedented resolution, and reveal how disruptions in these processes lead to inflammation and disease. Using cutting-edge omics and artificial intelligence to augment tissue-based systems, the CZ Biohub Chicago will uncover new insights into how inflammation begins and how it can be controlled.
Inflammation and overactive immune cells play a key role in many diseases, including cancer, heart disease, and Alzheimer’s disease, and are also implicated in organ failure, and severe infectious diseases like COVID-19. But inducing inflammation in a controlled way can also be used to combat disease: in cancer immunotherapy, the immune system is unleashed and directed toward tumors. The CZ Biohub Chicago’s first explorations of inflammatory processes will involve human skin tissue, as many skin diseases are driven by inflammation.
Through advances in genomics, molecular biology, and most recently, single-cell biology, scientists have made great strides in understanding the structure and function of individual cells. But our organs are made up of specialized tissues that contain billions of cells — our heart muscle alone is estimated to comprise more than two billion cells — so gaining insights about how tissues work as a whole, in both health and disease, is an enormous challenge.
To begin to crack this problem, the engineered platforms that are under development at the CZ Biohub Chicago are combining state-of-the-art technologies to make the first holistic and direct measurements of inflammation in human tissue. These tools will allow researchers to monitor the activity of immune cells within tissues in real time, with the goal of finding ways to steer the immune system away from the “tipping points” that lead to inflammatory disorders. With a more comprehensive understanding of this biology, new approaches to treating a range of diseases will be made possible, with the ultimate aim of making inflammation-driven diseases more treatable and preventable.
Learn more